Introduction
Blood is made up of:
- RBCs,
- White blood cells (WBCs),
- Platelets
These are suspended in plasma. RBCs have hemoglobin, which carries oxygen throughout the body to all of the tissues and organs. An RBC is pale red and gets its native color from hemoglobin. It’s shaped like a doughnut, but it has a thinner area in the middle instead of a hole. The RBCs are normally all the same color, size, and shape. However, certain conditions can cause variations that impair their ability to work properly.
The Red blood cell Indices measure the size, shape, and physical characteristics of the RBCs. The doctor can use RBC indices to help diagnose the cause of anemia. Anemia is a common blood disorder in which there is too few, misshapen, or poorly functional RBCs.
Anemia can occur if:
- Very few RBCs are created, which is called aplastic anemia
- A significant blood loss occurs, such as in cases of hemorrhage.
- RBCs are destroyed prematurely, which is called hemolytic anemia
Platelets enable clot formation.
Red blood cell Indices include
The three most common indices are:
- The MCV,
- The MHC and
- The MCHC.
- Red cell distribution width (RDW)
1. Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)
The Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) is the average volume of a single red cell expressed in femtoliters (FL) or 10^ -15 L. It helps in determining the size of the RBC. The PCV and red cell volume are used in its calculation.
Reference Range
The MCV reference range is 83-101 fl. The MCV is increased in macrocytic anemias (e.g megaloblastic anemia) and decreased in microcytic anemias (e.g. iron deficiency, thalassemia)
- MCV value is within the normal range – Normocytic.
- MCV value is above the normal range – Macrocytic.
- MCV value is below the normal range – Microcytic.
2. Mean Cell Hemoglobin (MCH)
Mean Cell Hemoglobin (MCH) is the average weight in picograms of Hb in one red cell. The Hb level an(d the RBC count are used for calculation.
Reference Range
The MHC reference range is 27-32 pg. MHC is increases in macrocytic anemia and decreased in microcytic anemias.
- MCH value is within the normal range Normochromic
- MCH value is above the normal range – Hyperchromic
- MCH value is below the normal range -Hypochromic
3. Mean Cell Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC)
The MCHC is the concentration of Haemoglobin per unit volume of red blood cells expressed as a percentage, g/dl or g/l. Hemoglobin and PCV are required to calculate MCHC
Reference Range
The reference range for MCHC is 32-36 g/dl or (320-360 g/l). A fully saturated red cell has a hemoglobin concentration of 36 g/dl. MCHC is a useful guide to the degree of hypochromia present in iron deficiency anemia. The Hb and PCV can be estimated reasonably accurately and the derived MCHC is therefore a reliable parameter.
4. Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW)
Red cell distribution width (RDW) is a assesses the variability in the size of the red blood cells. A normal RDW means that red blood cells are all similar in size, whereas a higher RDW means that there is more variability in the size of the red blood cells. This is called anisocytosis. RDW values are described in percentages. It is instead calculated as the standard deviation of red blood cell volume/mean cell volume) × 100.17
A normal reference range for RDW is 11.5% to 14.5%.18
A low RDW means that red blood cells are not very different in size from typical measurements. A high RDW means they differ in size more significantly, which can indicate the body is not properly producing enough red blood cells.
The interpretation of the RDW differs from the other blood tests in that it varies based on its relationship to the MCV. In short, the sizes and variability of red blood cells can indicate vastly different things.
Automated Estimation of Red Blood Cell Indices
In automated counters, MCV is measured directly, but in semi-automated counters MCV is calculated by dividing the PCV by RBC. MCH is derived from the Hb divided by RBC. The MCHC is derived from the Hb and the PCV with instruments that measure the PCV and calculate the MCV, whereas when the MCV is measured directly and the PCV is calculated, the MCHC is derived from the Hb, PCV and RBC.
In summary
Red blood cell indices are like the battery of tests that give information about measurable characteristics of red blood cells, including their size and the concentration of hemoglobin in them. The tests include t
- The mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC),
- Mean corpuscular volume (MCV),
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH),
- Red cell distribution width (RDW).
The test values can give a healthcare provider in the direction of the possible causes when compared to each other or to other blood, lab, or imaging test reports.
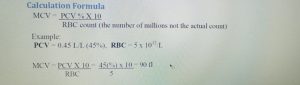



1 thought on “How Red Blood Cell Indices are Calculated”